Frequently Asked Questions
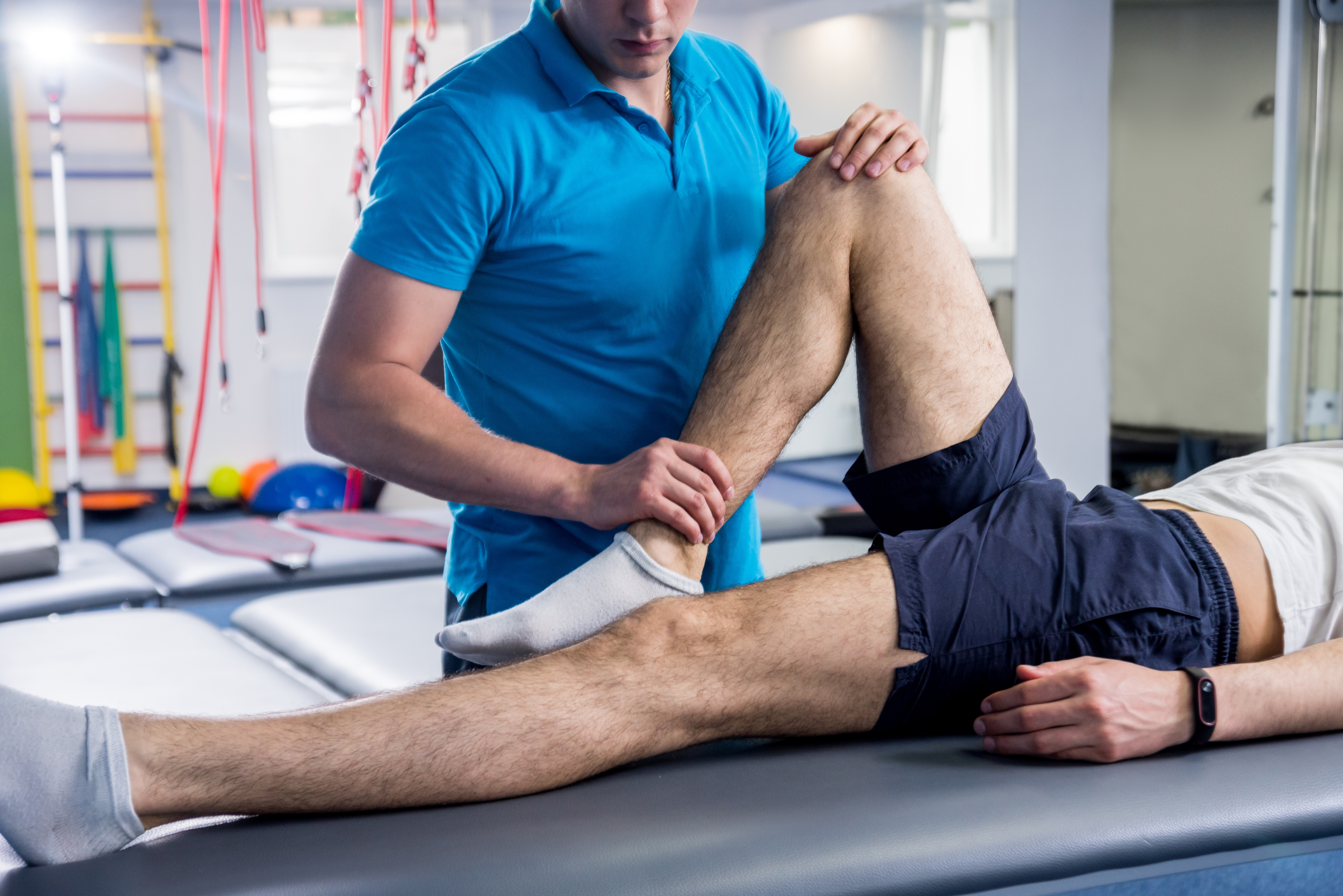
Physical therapists employ a variety of specialized techniques to enhance range of motion following joint surgery, focusing on individualized rehabilitation protocols. These may include passive and active assisted stretching exercises aimed at increasing flexibility and preventing stiffness in the affected joint. They often incorporate modalities such as heat therapy or cryotherapy to reduce inflammation while improving circulation during treatment sessions. Manual therapy techniques like mobilization are utilized to promote synovial fluid movement within the joint capsule, facilitating better articulation. Additionally, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) methods can further support muscle elongation and functional stability around the surgically repaired area. Strengthening regimens that emphasize eccentric and concentric contractions also play a critical role in restoring balance between agonist and antagonist muscles postoperatively, ensuring optimal recovery outcomes with enhanced mobility over time.
Physical therapy can effectively address muscle imbalances in patients with chronic lower back pain through a comprehensive approach that includes targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, and postural education. By assessing the patient's functional movement patterns and identifying specific areas of weakness or tightness, physical therapists can develop individualized rehabilitation programs aimed at strengthening underactive muscles while stretching overactive ones. Techniques such as neuromuscular re-education promote proper biomechanics and alignment, thereby reducing strain on the lumbar spine. Additionally, modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation may be incorporated to facilitate recovery and enhance muscular activation. Overall, this tailored intervention not only alleviates pain but also restores core stability and improves overall musculoskeletal function, ultimately leading to enhanced quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic lower back discomfort due to muscle imbalance issues.
Evidence supporting the effectiveness of aquatic therapy for post-operative knee rehabilitation includes numerous studies demonstrating improved range of motion, strength, and functional mobility among patients recovering from knee surgeries such as arthroscopy or total knee replacement. Research indicates that hydrotherapy facilitates lower impact exercises due to buoyancy, which reduces joint stress while promoting muscle activation and cardiovascular conditioning. Additionally, the unique properties of water—such as resistance training through varying movements in a pool environment—enhance proprioception and balance recovery. Clinical trials have shown significant reductions in pain levels and swelling when compared to traditional land-based rehabilitation methods, highlighting improvements in overall patient outcomes like gait analysis metrics and quality of life assessments. Furthermore, patient adherence rates are often higher during aquatic sessions due to the enjoyable nature of exercising in water, contributing positively to long-term rehabilitation success.
Neuromuscular re-education is pivotal in the recovery from shoulder injuries as it focuses on restoring proper movement patterns, enhancing proprioception, and improving muscle coordination. Through targeted exercises that promote neuromuscular control and stability, individuals can regain functional range of motion while addressing deficits in strength and balance. Techniques such as electrical stimulation may also be employed to facilitate motor learning and engagement of specific musculature around the glenohumeral joint. By retraining neural pathways involved in shoulder mechanics, patients experience a reduction in compensatory movements that often lead to chronic pain or further injury. Additionally, incorporating principles of kinetic chain rehabilitation allows for comprehensive integration of scapular stabilization with rotator cuff strengthening interventions, ultimately fostering optimal biomechanical function during activities of daily living or sports performance post-injury.
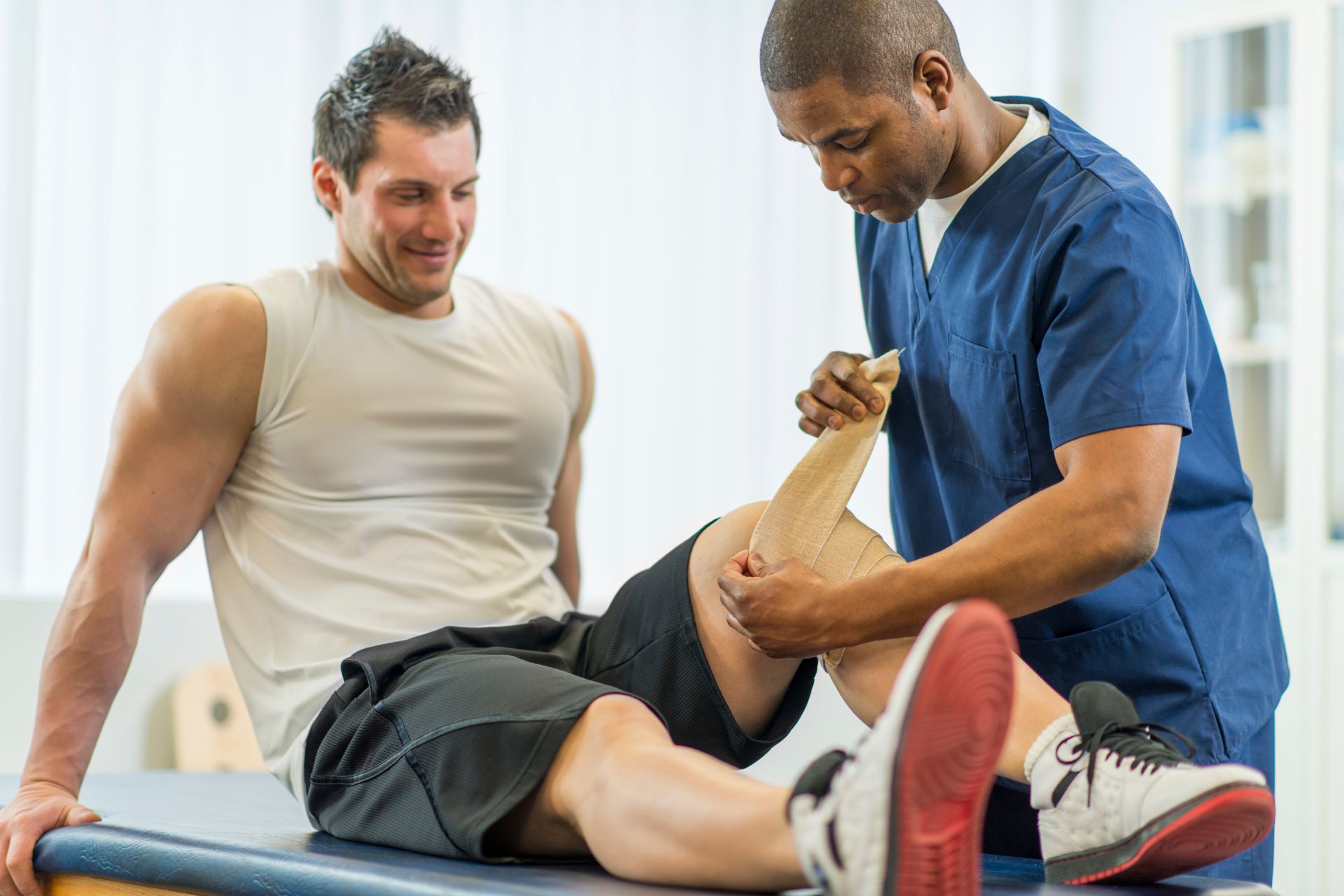
Personalized exercise regimens in physical therapy significantly enhance recovery outcomes for athletes rehabilitating from sports-related fractures by addressing individual biomechanical needs, specific injury mechanisms, and personal fitness levels. Tailored therapeutic exercises facilitate optimal muscle strength restoration, joint stability improvement, and functional mobility enhancement while minimizing the risk of re-injury. By incorporating sport-specific movements and techniques into rehabilitation protocols, therapists can ensure a gradual return to performance standards required in competitive environments. This individualized approach often includes progressive resistance training, proprioceptive drills for neuromuscular coordination, and flexibility workouts designed to restore range of motion effectively. Furthermore, integrating psychological support through motivational strategies helps maintain athlete engagement throughout the rehabilitation process. Ultimately, personalized care plans promote not only physical healing but also confidence rebuilding essential for successful reintegration into sports activities post-fracture recovery.